Last update : August 9, 2012
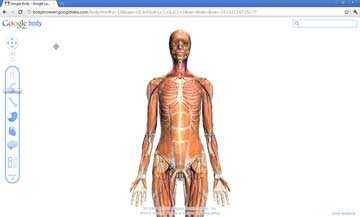
Google Bodybrowser
On December 15th, 2010, Google announced the launch in Google Labs of an interesting WebGL application called Body Browser, which lets you explore the human body just like you can explore the world in Google Earth.
Google Body (Google Human) is a detailed 3D model of the human body. You can peel back anatomical layers, zoom in, click to identify anatomy, or search for muscles, organs, bones and more. You can also share the exact scene you are viewing by copying and pasting the URL.
To view the body application, you need a Web browser that supports WebGL. I use Google Chrome.
The 3D body data was provided by the Zygote Media Group, Inc., a leading company in the development of Bio-Medical 3D content (since 1994).
Zygote offers stock 3D models, images and animation of the Human Anatomy Collections through the website 3DScience.com. These collections are the best and most comprehensive available. The artistic and illustrative value is unquestionable while remaining medically accurate.
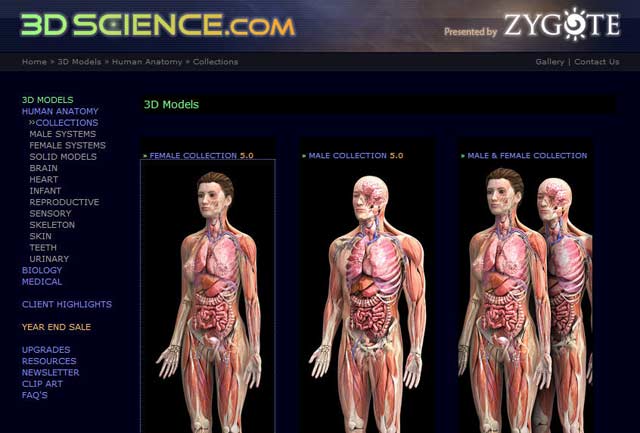
3D anatomy collection of Zygote
Late 2011, the Google Body application was disabled. A commercial 3D platform BioDigital Human that simplifies the understanding of anatomy, disease and treatments has been launched in the meantime by Biodigital. Founded in 2002, BioDigital is the leading developer of state of the art biomedical visualization systems.