Last update : August 27, 2013
The best known musical scores library is IMSLP (International Music Score Library Project), also called the Petrucci Music Library, after publisher Ottaviano Petrucci. IMSPL is a project for the creation of a virtual library of public domain music scores, based on the wiki principle. It was launched on February 2006 by Edward W. Guo (pseudonym Feldmahler), a graduate of the New England Conservatory and Harvard Law School.
Links to other musical scores library are provided in the following list :

Vladimir Viro & Michael Scott Cuthbert at the 1st Classical Music Hack Day, Vienna 2013 – Photo by Thomas Bonte
Vladimir Viro, a computer scientist at the Ludwig-Maximilians University in Munich, Germany, is founder and lead developer of Peachnote, a classical music search tool. Vladimir Viro published a research paper on Peachnote at the 12th International Society for Music Information Retrieval (ISMIR) conference in 2011. The service enables a user to freely search IMSLP, the US Library of Congress, and other archives for classical music. Peachnote uses a music N-gram Viewer, that’s analogous to Google’s N-gram Viewer.

Werner Schweer, Hervé Bitteur, Nicolas Froment, Thomas Bonte at the 1st Classical Music Hack Day, Vienna 2013
Michael Scott Cuthbert, Associate Professor of Music at MIT and creator of music21, a flexible toolkit for computer-aided musicology, is impressed by the impact of Peachnote on musicology.
Vladimir Viro and Michael Scott Cuthbert presented their projects at the 1st Classical Music Hack Day which took place at the mdw-University of Music and Performing Arts in Vienna, February 1st – 3rd, 2013. Werner Schweer, Nicolas Froment and Thomas Bonte presented at the same days their free open-source musical notation program MuseScore.
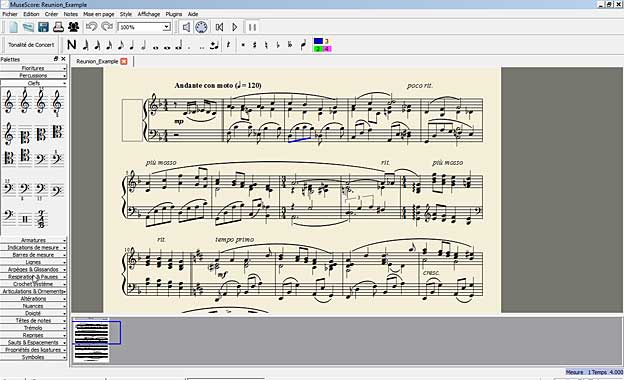
MuseScore open-source program
An alpha version of an embeddable score viewer is provided by Peachnote :

Peachnote Score Viewer
Links to additional informations about Peachnote, music21 and MuseScore are listed hereafter :