Last update : August 9, 2013
eyePlorer by Vionto
eyePlorer is (or was) a graphical knowledge engine created by vionto®. Current search engines only present lists of links and documents, with eyePlorer however, you are able to locate relevant information and connections instantly. Facts and relationships between terms and concepts are visualised in an interactive application. The knowledge machines build by vionto® employ sophisticated semantic techniques in order to analyse the meaning of sentences and texts. The benefit for the user is that he or she can work with individual facts instead of just long documents.
The user does not work with documents but with knowledge and facts in a graphical, interactive, almost dialogue-like kind of way. Knowledge is visually arranged in different categories. vionto® knowledge machines are based on semantic analyses derived from cognitive science, brain research and computational linguistics. vionto® relies on a robust language technology platform and sophisticated linguistic resources such as, for example, ontologies and thesauri. Currently eyePlorer processes the English and German Wikipedia as well as MEDLINE/PubMed.
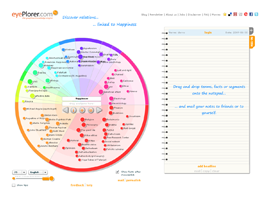
In the circular area on the left hand side eyePlorer presents eyeSpots – these represent terms that are related to a search topic. The exact nature of these connections can be displayed by pointing or clicking on an eyeSpot. A small window, the eyeTip, opens and displays facts that document the relation with one or more facts taken from our knowledge base. The circular area filled with eyeSpots that relate to a certain search term is called an eyeMap. To display connections between eyeSpots just double-click on an eyeSpot – lines will appear between the eyeSpot you clicked upon and eyeSpots that are semantically related. A click on one of these lines will display associated facts taken from the knowledge base.
EyeSpots are associated with various categories (people, countries, organizations, time, society, work, science & technology, …) visualized with different colors. The categorisation is a procedure that is carried out automatically. A double click on an empty area of a category expands it and shows only this category along with all its subcategories.
A dynamic link to eyePlorer can be added to a website to visualize search terms.
vionto® filed for U.S. patent registration of the eyePlorer technology. The eyePlorer visualizes knowledge graphs (k-graphs) derived from various contents that can be interactively explored.
vionto GmbH was founded in december 2008 in Berlin by Ralf von Grafenstein (Diplom-Kaufmann) and Dr. Martin C. Hirsch (neurobiologist and brain researcher). The first version of eyePlorer went online in February 2009 (see Frankfurter Allgemeine Feuilleton : Google-Herausforderer eyePlorer – Die Welt ist doch eine Scheibe) . Several prestigious prizes of the internet sector have been awarded to vionto® (SUMA award, ECO Intenet award, Red Herring Europe Top 100 2009 Award, …)
However one year later was the end of the prestigious project with the inglorious death by bankruptcy of vionto GmbH (see SpeedX Blog : Verglüht). It was the same destiny as its ancestor semgine GmbH. The successor seems to be medx GmbH (diagnostic reasoning), the url eyeplorer.com is redirected to this site.