A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom, distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Atoms are build of particles.
Isotopes are atoms of the same element (same number of protons), but having different numbers of neutrons. Most naturally occurring elements (66 of 94) have more than one stable isotope. For example, there are three main isotopes of carbon. All carbon atoms have 6 protons in the nucleus, but they can have either 6, 7, or 8 neutrons. Since the mass numbers of these are 12, 13 and 14 respectively, the three isotopes of carbon are known as carbon-12 (12C), carbon-13 (13C), and carbon-14 (14C). Carbon in everyday life and in chemistry is a mixture of 12C, 13C, and a very small fraction of 14C atoms. Its presence in organic materials is the basis of the radiocarbon dating method to date archaeological, geological, and hydrogeological samples.
The tabular display of the chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties is called the periodic table. Although precursors exist, Dmitri Mendeleev is generally credited with the publication, in 1869, of the first widely recognized periodic table.
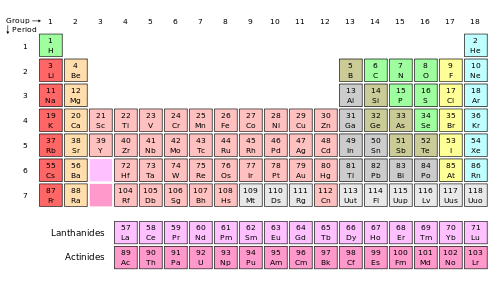
Periodic table of chemical elements (Wikipedia)
As of 2012, the periodic table contains 118 confirmed chemical elements.The latest, ununseptium, has been identified in 2010. Of these 118 elements, 114 have been officially recognized and named by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). A total of 98 are known to occur naturally on earth. 80 of them are stable, while the others are radioactive, decaying into lighter elements. A detailed list of the 118 known chemical elements is available at Wikipedia.
The lightest of the chemical elements are hydrogen and helium, both created by the Big Bang nucleosynthesis during the first 20 minutes of the universe. They are by far the most abundant chemical elements in the universe. However, iron is the most abundant element making up the earth, and oxygen is the most common element in the earth’s crust.
Although all known chemical matter is composed of chemical elements, chemical matter itself constitutes only about 15% of the matter in the universe. The remainder is dark matter, a mysterious substance which is not composed of chemical elements.
When two distinct elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, the result is termed a chemical compound. Two thirds of the chemical elements occur on earth only as compounds. Just six elements – carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, calcium, and phosphorus – make up almost 99% of the composition of a human body.
